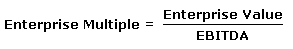The target is Boeng Company (NYSE : BA)
and selected trading comps are Lockheed Martin Corporation (NYSE :
LMT) and Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE : NOC) . Although the
target is BA, opinions and price targets are determined for every
trading comps' stock.
Thereby, suggestions are made for a
3-month investment and a longer-term 1-year investment.
Data dates back to
February 4th, but this will not affect anything about the estimate,
because the multiples and price have remained similar.
The 2013-year comparison between The Boeing Company, Lockheed Martin Corporation and Northrop Grumman Corporation on February 4th.
|
Trading Multiple |
BA |
LMT
|
NOC |
Mean(average) |
|
Current share price |
122.8 |
148 |
111.4 |
- |
|
% of 52-wk.high |
85% |
91% |
90% |
- |
|
Enterprise Value
|
93 210 mln. |
8 453 mln. |
28 881 mln. |
- |
|
P/E |
24 |
16.4 |
13.3 |
17.9 |
|
P/S |
1.09 |
1.1 |
0.98 |
1.06 |
|
P/B |
24.8 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
EV/EBITDA |
14.2x |
1.88x |
5.37x |
7.15x |
|
EV/SALES |
1.08x |
0.18x |
1.17x |
0.81x |
|
Leverage |
1.47x |
1.37x |
1.42x |
1.42x |
|
ROE |
43.7% |
120% |
19.4% |
61% |
|
ROA |
0.51% |
8.0% |
7.4% |
5.3% |
|
Gross margin |
7.6% |
9.9% |
21.8% |
13.1% |
|
EBITDA margin |
15.4% |
9.2% |
12.7% |
12.4% |
|
Net profit margin |
5.3% |
6.6% |
7.9% |
6.6% |
|
Ex-dividend
|
N/A |
2.10% |
1.80% |
- |
|
Dividend Yield |
12.02.2014 |
27.02.2014 |
27.11.2013 |
- |
|
Opinion |
Strong Buy |
Sell |
Hold
|
- |
|
Price target |
150$
|
140$
|
120$
|
- |
- Next 3-month recommend to BA, because it had disappointing 4th quarter results, but RSI has fallen to 30-40 zone. Although EBITDA has suffered because of operating expenses, its COGS (cost of goods sold) still have not been suffering. It is indicated by the increase of EV/EBITDA and Gross profit margin. Its asset base compared to liabilities is still much stronger than its trading comps' NOC and LMT.
- Next 1-year recommend to NOC, because it shows high margins for a company smaller than Boeing, which are great indicators for future positively surprising results. Although NOW has risen 85% since January 2013 and a correction down to 100pt should be expected, the long-term investment bought from 100pt level is recommended. Equivalently it has lower P/E and P/S than its trading comps. Sure, P/B is negative, because NOC has higher liabilities than assets. That ought not to affect high margins and earnings growth, unless the whole economic starts to stumble as feared. If market is feared to be crashing, the price target should be approximately divided by three, because this is were